2D drawings remain important in manufacturing and engineering, especially in the context of technical drawings, schematics, blueprints, and other forms of documentation. While 3D modeling has brought significant advancements and benefits to the field, 2D drawings remain the tangible item that anyone is able
Are 2D Drawings a Thing of the Past?

Today, 2D drawings are still used in both the engineering and manufacturing arenas. While some may believe that 2D drawings are falling the way of the dinosaur, we still need them to show details in parts, components, and assemblies. They are a fundamental part of engineering documentation. Manufacturers use 2D drawings as their main communication tool. In this blog, we will explore the reasons we believe that 2D drawings will remain an important modeling tool for engineering projects.
The Evolution of 2D Drawings:
Before there were computers, 2D drawings were used to define component specifications. With 2D drawings, engineers were able to navigate the creation of a product, simply by referencing the 2D rendering. The 2D drawing method of production dates to the beginnings of engineering information. Today, this history speaks to the importance of 2D drawings.
As 2D drawings were the sole conveyor of design information for millennia. That all changed with the introduction of computers and 3D software like Autodesk Inventor, and SolidWorks. The choice of CAD software depends on your specific needs and the industry you're working in. You may want to consider factors like your budget, the type of projects you'll be working on, and your familiarity with the software when selecting the right CAD program for your needs.
But before we look at 3D technology, let’s examine the things that are still relevant today with 2D drawings.
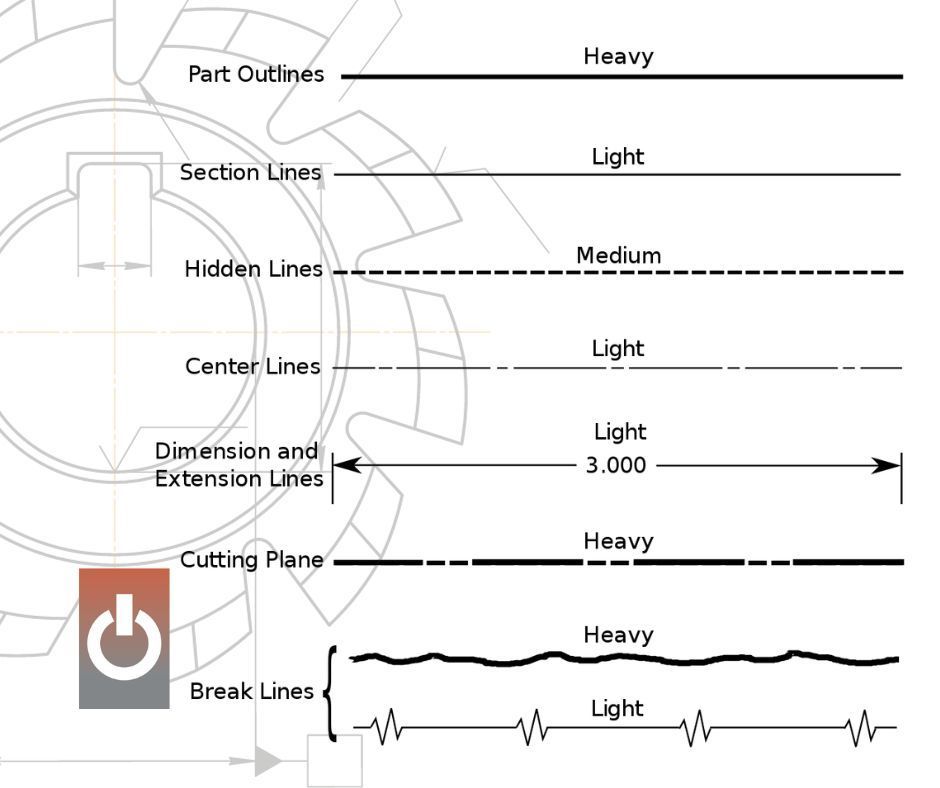
2D Drawings Are Better at the Details:

2D Drawings Continue to Serve Critical Purposes:
- Clear Documentation: 2D drawings are crucial for creating technical drawings that provide clear and precise instructions for manufacturing and assembly. These drawings convey essential details, dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications required for producing a component or product accurately.
- Standard Representation: Many industries and regulatory bodies still rely on traditional 2D engineering drawings as the standard form of representation. These standardized drawings ensure uniformity and ease of interpretation across different stakeholders involved in the manufacturing process.
- Legacy Systems and Processes: Numerous manufacturing processes, especially in established industries, are based on legacy systems and workflows that primarily use 2D documentation. Transitioning completely to 3D software may require significant investments in new tools and training, making 2D drawings necessary for maintaining existing processes. Our IT department can help you with legacy system integration. Learn more HERE.
- Simplicity and Clarity: In some cases, 2D drawings are simpler and more efficient for representing certain aspects of a design. For straightforward components or for conveying specific details quickly and clearly, a 2D representation can be more effective than a complex 3D model.
- Ease of Printing and Distribution: 2D drawings are easy to print, share, and distribute, especially in a paper-based format. They can be shared via email, included in reports, or printed for use in various stages of production, making them highly practical and accessible.
- Historical Data and Archives: Many organizations have an extensive archive of 2D drawings and documents that contain valuable historical data. These records are often necessary for maintenance, repairs, or improvements, making 2D drawings indispensable for reference and continuity.
- Integration with Existing Processes: 2D drawings are well-integrated into many existing engineering and manufacturing processes, including software systems and tools that are designed around 2D representation. These processes may not easily transition to a completely 3D-centric workflow.
"At this point, 2D drawings will still be relevant and useful in some respects, but the time we spend perfecting them or communicating information through them will be as small as possible. “ -Trevor English, Interesting Engineering
3D Revolutionized Design.
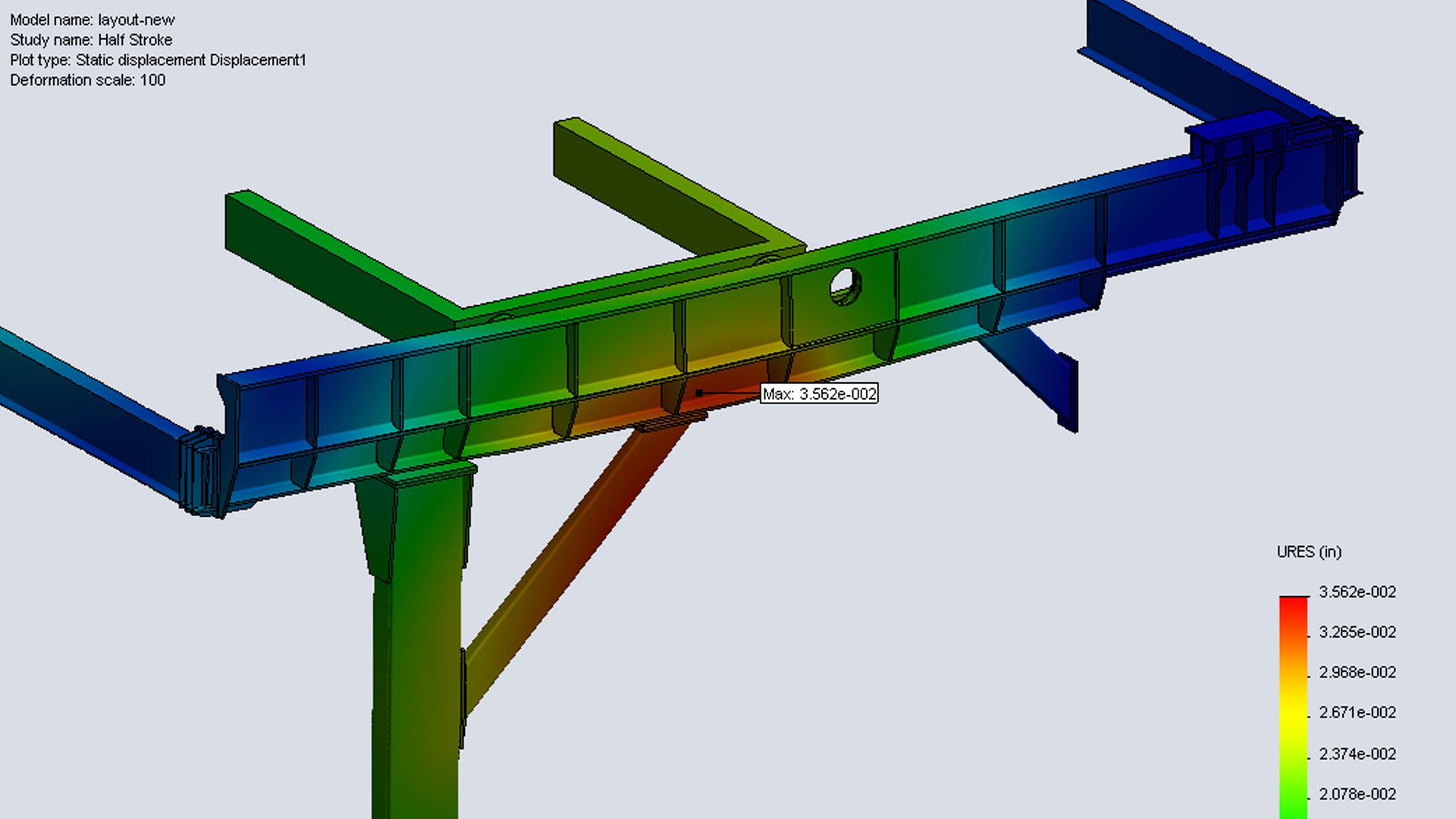
3D modeling has revolutionized the field of engineering in numerous ways, fundamentally changing the way engineers design, analyze, and communicate their ideas. Technology has expanded the capabilities of the way that engineers design and prototype. Seifert Technologies Engineering division embraced the tectonic shift with the emergence of new tools. Today, the engineers at Seifert continue to bring ideas to life through both 2D design and 3D renderings.
Ways 3D Modeling Has Impacted Engineering:
- Visualization and Design Iteration: 3D modeling allows engineers to create highly detailed and accurate visual representations of their designs. This enables them to visualize the final product or structure in a realistic manner, aiding in better decision-making and design iteration before physical prototypes are created.
- Improved Design Accuracy and Precision:3D modeling provides engineers with precise measurements, angles, and dimensions, enhancing design accuracy. Engineers can create complex geometries with detailed features, ensuring components fit and function as intended.
- Rapid Prototyping and Testing: 3D models can be used to create physical prototypes using 3D printing or other rapid prototyping technologies. This accelerates the product development cycle by allowing engineers to quickly test and validate their designs, identify issues, and make necessary improvements.
- Simulation and Analysis: 3D models can be integrated with simulation software to analyze and simulate the behavior of a product or structure under various conditions. This helps engineers optimize designs for factors such as stress, heat distribution, fluid flow, and other parameters, ensuring the final product meets performance requirements.
- Collaboration and Communication: 3D models facilitate better communication and collaboration among multidisciplinary teams. Engineers can share 3D models with colleagues and clients, making it easier for everyone to understand the design, offer feedback, and make informed decisions collectively.
- Cost and Time Savings: By allowing engineers to identify and address design flaws early in the development process, 3D modeling reduces the costs associated with correcting errors during later stages of production. It also accelerates the design process, leading to faster time-to-market for products.
- Customization and Personalization: 3D modeling enables engineers to easily customize designs to meet specific client requirements or adapt to unique conditions. This is particularly important in industries where customization or personalization is essential, such as medical devices or automotive components.
- Digital Twin Concept: Engineers use 3D models to create digital twins of physical assets or systems. This virtual representation allows real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization of the physical counterpart, leading to enhanced efficiency, maintenance, and sustainability.
- Automation and Artificial Intelligence Integration: With advancements in AI, engineers can use 3D models as input for machine learning algorithms. AI can assist in automating design tasks, generating design options, predicting performance, and optimizing designs based on specified criteria. You can read more about this in our blog HERE.
How Can Seifert Technologies Help?
While 3D modeling has significantly impacted engineering by enhancing visualization, improving accuracy, accelerating the design process, enabling simulations, facilitating collaboration, and ultimately leading to more efficient and effective product development. 2D drawings still play an important role in both engineering and manufacturing. Although now a days 3D is preferred, our engineers at Seifert Technologies have the expertise to tackle a project using 2D or 3D.